Originally published
on 12/20/2021
Drug Pricing Lab

The payment mechanisms and existing policies that govern how drug prices are determined and passed through the supply chains are poorly understood and may have important consequences for the potential impact of such reforms in the domestic context.
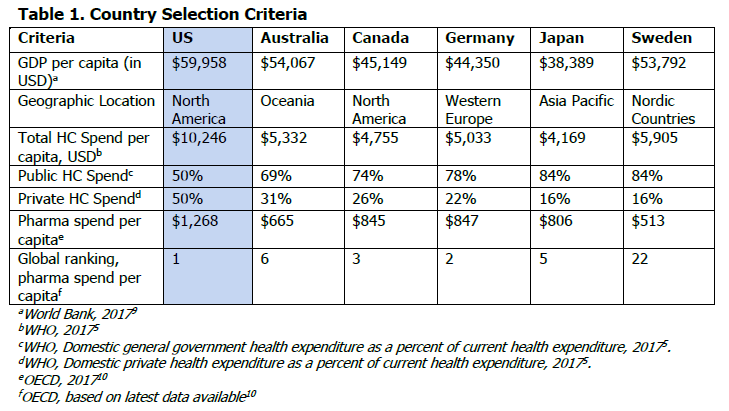
In this Drug Pricing Lab report, we compare the unique levers in the price negotiation process and supply chains of the US, Canada, Germany, Sweden, Australia, and Japan that allow for different prices for the same products. Countries were selected based on their economies, geography, healthcare delivery, and prescription drug spending. Targeted literature reviews examined the journey of specialty self-administered drugs from initial marketing approval to patient dispensing, which were used to develop discussion guides for interviews with in-country experts.
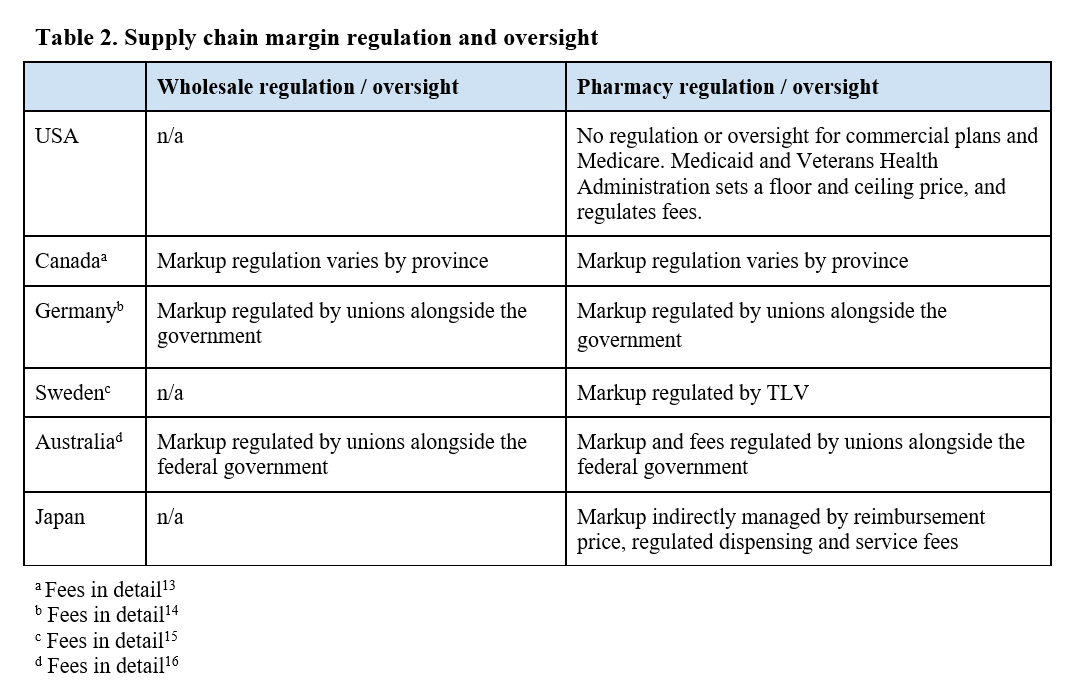
Country-specific findings were compared using an internal assessment tool designed to capture information about each step of a drugs’ journey (Table 1). Compared to the US, other countries establish a single price through negotiation, and ensures that this is the benchmark price throughout the supply chain. In doing so, the ability for pharmacies and wholesalers to benefit from markups and spread pricing on high-priced products is limited, and the need for third-party administrators so heavily utilized in the US, are non-existent (Table 2).
Proposals to reform US prescription drug prices by adopting negotiating strategies used in other countries should consider how these countries pull prices through their supply chains. Reforms in the absence of such policies may result in fewer savings than hoped; coupled with them, they might be further amplified.
Read the full report here.